The One question that is raging across the country is why are we seeing COVID positive cases in people even after vaccination of 2 doses
The answer to that question lies buried in the scientific literature of the landmark trials of the vaccine. Before I proceed with explanation of that, there is no doubt that VACCINATION saves lives. A little more about that later.
So let us look at the 2 vaccines available in India. COVISHIELD manufactured by Serum Institute of India ( the equivalent of Astra Zeneca- Oxford vaccine) and COVAXIN manufactured by Bharat Biotech.

The COVISHIELD is an adenovirus vector Vaccine (more details can be found here) and the Bharat Biotech COVAXIN is a killed virus vaccine along with immune-potentiators, also known as vaccine adjuvants such as Aluminium and Imquimod.
The other vaccines across the world are the mRNA vaccines of Pfizer and Moderna. Recently Russia’s Sputnik V which is a recombinant adenovirus vector vaccine was approved in India.
So what did the trials show regarding prevention of infection?
Lets look at COVISHIELD. A Vaccine which majority of Indians have received and a full paper data is available.
The first publication of the Astra Zeneca trials done in UK, Brazil and UK used the end point of the study to be symptomatic COVID 19 virologically confirmed .
In other words , how many people who used the vaccine developed a symptomatic infection confirmed by a virological test as compared to those who did not use the vaccine. While there were many subgroups of dose and interval difference that impacted the overall vaccine efficacy ( discussed in this article: ), the efficacy of the vaccine was 70%.
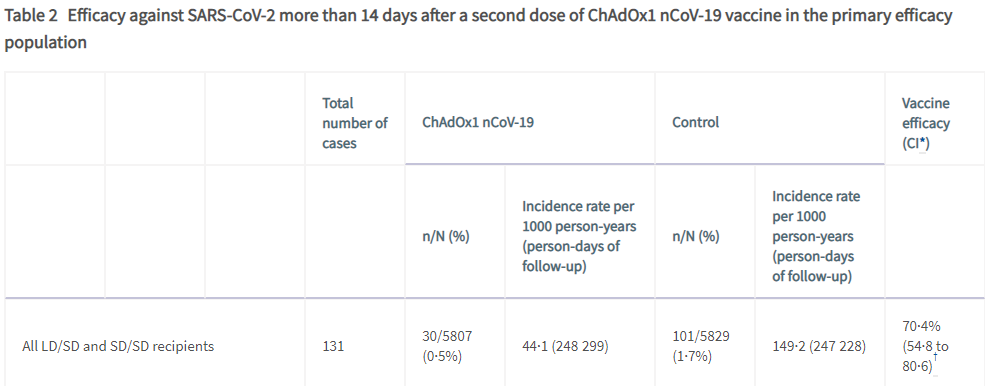
So how was this number of efficacy of 70% arrived at and what does it mean ?
Out of the 5807 who received the Astra Zeneca –oxford vaccine( COVISHIELD equivalent) 30 developed COVID-19 as compared to 101 subjects out of the 5829 who did not receive the vaccine.
This clearly tells us two things. That yes, even after vaccination it is possible to develop COVID-19 . A vaccine efficacy of 70% means that as compared to a person not vaccinated, the person vaccinated has a 70% less chance of developing symptomatic COVID 19.
But I hear about quite a few people developing COVID 19 2 weeks after 1st dose? How is this possible when the efficacy is 70% and more?
It is important point to realise the timeline which has been used to calculate the efficacy in the landmark trial.
These results were calculated 14 days after the Second dose which is when the vaccine protection starts to kick in.
The trial clearly shows us that the vaccine efficacy after 21 days of having received 1 standard dose is around 64%, less than the 70% achieved beginning 2 weeks after the second dose. 51 subjects developed symptomatic COVID 19 out of 6307 beginning from 21 days of the first dose of the vaccine as compared to 141 patients out of 6297 subjects.
So why take a vaccine then if one can still have a 30% chance of developing COVID-19?
The answer to that is simple. In this trial, it was clearly shown that there were More than 21 days after their first dose, ten participants were hospitalised due to COVID-19 (defined as WHO clinical progression score ≥4), two of whom were assessed as having severe COVID-19 (WHO score ≥6), including one fatal case.
All ten cases of hospitalisation were in the control group ie the group that did not receive the vaccine.
Hence it is demonstrated that vaccination protects from severe disease and hospitalisation which is what we want in a pandemic largely to prevent burdening of the healthcare system. These have been shown in trials of other vaccines too such as by data from Pfizer vaccination in Israel
Would it help in shortening the pandemic?
There are some interesting data coming out from certain studies. As mentioned on the CDC website: Preliminary data from Israel suggest that people vaccinated with the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine who develop COVID-19 have a four-fold lower viral load than unvaccinated people.29 This observation may indicate reduced transmissibility, as viral load has been identified as a key driver of transmission
In a preprint in Lancet by Astra Zeneca regarding their vaccine (COVISHIELD equivalent) , they highlight that in their analysis the potential for the vaccine to reduce asymptomatic transmission of the virus was found based on weekly swabs obtained from volunteers in the UK trial. The data showed that PCR positive readings were reduced by 67% (CI: 49%, 78%) after a single dose.
Thus based on preliminary data, vaccination would help in reducing the transmission and case load and thus contribute beneficially to the pandemic.
What about the efficacy of COVAXIN and Sputnik-5 vaccine?
We still do not have the complete results of the COVAXIN. The interim results of the Phase 3 trials showed that beginning 14 days after the second dose :
36 cases of COVID-19 were observed in the placebo group versus 7 cases observed in the BBV152 (COVAXIN®) group, resulting in vaccine efficacy of 80.6%.
There is some preliminary data of analysis from the National Institute of Virology indicates that vaccine-induced antibodies can neutralize the UK variant strains and other heterologous strains.
This maybe due to the fact that COVAXIN generates antibodies against different antigens of the COVID19 virus such as the Spike protein, the Nucelocapsid protein and the Receptor binding domain protein. However it is again important to keep in mind the duration required for seroconversion that is generation of antibodies.
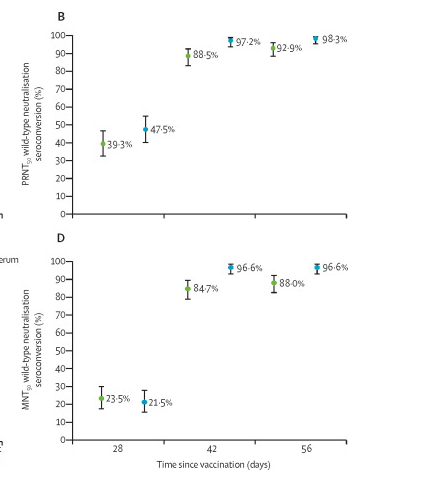
Based on their Phase 2 data published in Lancet with regard to time taken to generate antibodies against the above mentioned antigens of COVID19: between 60-70% approximately seroconverted on Day 28 that is 4 weeks from the first dose increasing to more than 90% from Day 42 ( ie 2 weeks after 2nd dose). High Neutralising anitbodies seroconversion of more than 90% was seen only after 2 weeks of 2nd dose ie on Day 56.
The Sputnik 5 has shown an efficacy of 91% beginning 21 days after the first dose. However it is also worth noting that 63 patients had COVID 19 less than 21 days after first dose of the vaccine.
So what are the take home points?
1.Vaccines are protective and have an efficacy ranging from 70%-90% depending on the type of vaccine used and the dosing interval in protecting from symptomatic COVID-19.
2.It takes time for formation of antibodies and most of the vaccine efficacy of vaccines in use in India has been calculated based on the incidence of Covid 19 occurring 2 weeks after the 2nd dose. Hence it should not be surprising to hear news of anyone testing positive before that.
3.It is still possible for a small number of subjects to develop COVID-19 even after 2 doses of the vaccine.But it is important to remember that some Trials have shown 100% protection against severe disease and Hospitalisation thus not only saving lives but easing the burden on the healthcare system .
Follow COVID appropriate behaviour such as Mask wearing and Social distancing to avoid infection to self and others
Compiled by
Dr.Nitin Yashas
Medical Oncology Resident and Co-Founder TREAT by ALTERDOCTORS
Enlighten, Empower, Entertain
References:
- Voysey M, Clemens SA, Madhi SA, Weckx LY, Folegatti PM, Aley PK, Angus B, Baillie VL, Barnabas SL, Bhorat QE, Bibi S. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. The Lancet. 2021 Jan 9;397(10269):99-111.
- 2. Ella R, Reddy S, Jogdand H, Sarangi V, Ganneru B, Prasad S, Das D, Raju D, Praturi U, Sapkal G, Yadav P. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBV152: interim results from a double-blind, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 trial, and 3-month follow-up of a double-blind, randomised phase 1 trial. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2021 Mar 8.
- Logunov DY, Dolzhikova IV, Shcheblyakov DV, Tukhvatulin AI, Zubkova OV, Dzharullaeva AS, Kovyrshina AV, Lubenets NL, Grousova DM, Erokhova AS, Botikov AG. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. The Lancet. 2021 Feb 20;397(10275):671-81.